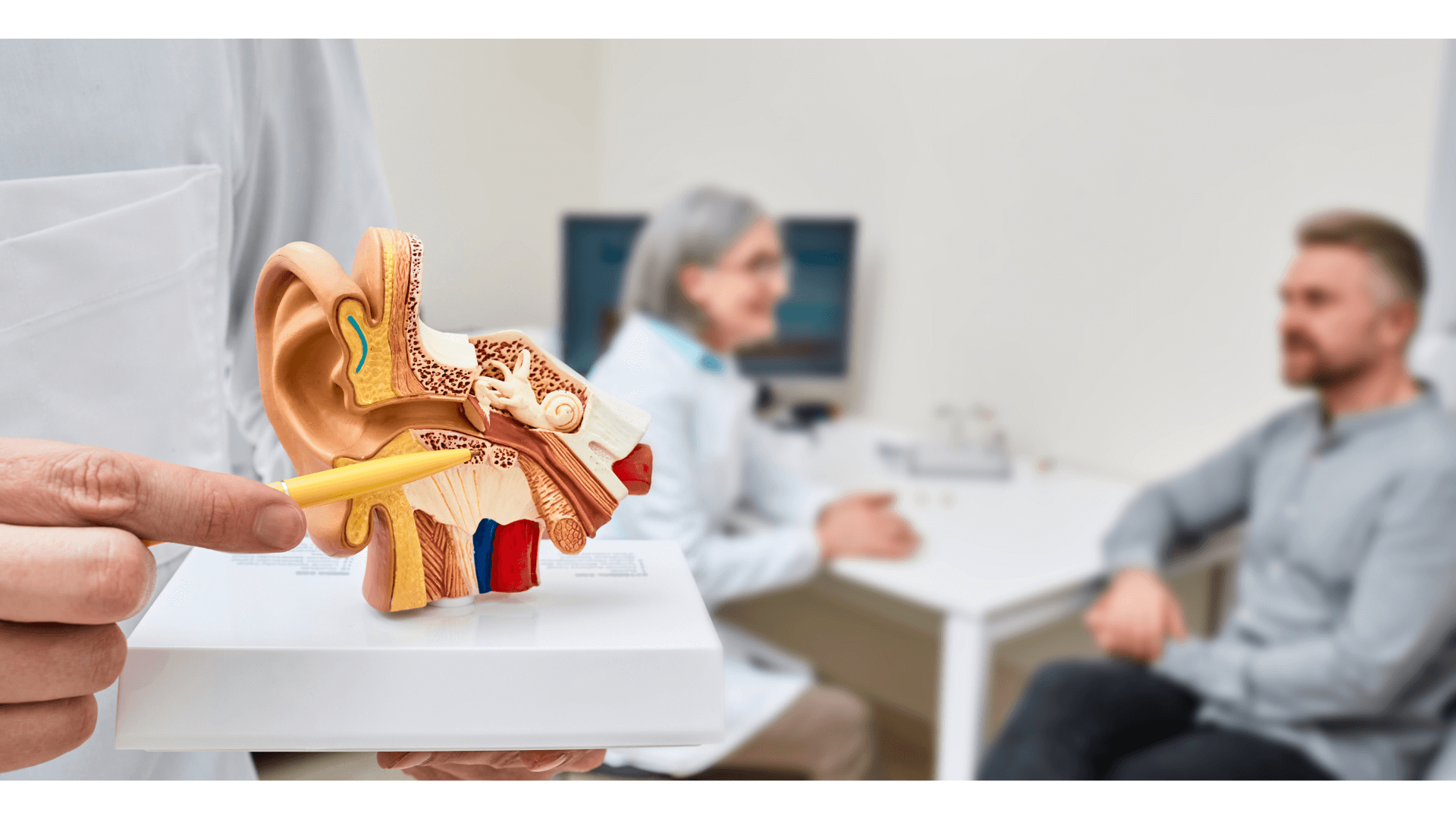
Hearing loss is a condition that can significantly affect your quality of life, impacting communication, social interaction, and overall well-being. One common type of hearing impairment is conductive hearing loss. This hearing loss is caused when sound is not effectively transmitted through the outer ear canal to the eardrum and the tiny bones of the middle ear.
Understanding Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when there’s a blockage or damage in the ear that prevents sound from reaching the inner ear. This form of hearing loss can be temporary or permanent, depending on the underlying cause.
Common Causes of Conductive Hearing Loss
Various factors may lead to conductive hearing loss, including but not limited to:
- Ear infections (otitis media)
- Fluid in the ear (often due to colds)
- Allergies
- Poor Eustachian tube function
- Perforated eardrum
- Benign tumors
- Impacted earwax (cerumen)
- Infection in the ear canal (external otitis)
- The presence of a foreign body within the ear
- Congenital absence or malformation of the ear canal or middle ear structures
Symptoms of Conductive Hearing Loss
The symptoms of conductive hearing loss can vary from person to person. Common indicators include:
- Muffled hearing
- Difficulty hearing faint sounds
- The feeling of fullness in the ear
- Ear pain or discomfort
- A sensation that the ear is “plugged”
- Frequent ear infections
- Discharge or odor from the ear
- Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ear)
Diagnosing Conductive Hearing Loss
If hearing loss is suspected, consulting with a healthcare provider or hearing health specialist is recommended. We perform a number of tests to find out more about your hearing loss and diagnose the kind of hearing loss you have.
Physical Examination
We will look into the ear using an otoscope to check for abnormalities such as blockages, earwax buildup, inflammation, and eardrum perforations.
Hearing Tests
Several hearing tests may be used to examine conductive hearing loss:
- Pure Tone Audiometry: Identifies the quietest sound a person can hear at various frequencies.
- Tympanometry: Assesses the functioning of the middle ear by applying varying air pressure in the ear canal.
- Acoustic Reflex Testing: Measures muscle contractions in the middle ear in response to loud sounds.
These tests can pinpoint the cause and extent of the hearing loss.
Treatment Options for Conductive Hearing Loss
The management and treatment of conductive hearing loss depend on its cause. Solutions range from medical intervention to surgical procedures.
Medical Treatments
- Earwax Removal: Simple, painless procedures can remove impacted earwax.
- Medication: Antibiotics or topical treatments are prescribed for infections.
- Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: Treatments like nasal sprays, decongestants, or autoinflation methods.
Surgical Procedures
In more severe cases, surgery might be necessary, such as:
- Tympanoplasty: Repairing a hole in the eardrum.
- Ossiculoplasty: Repair of the middle ear bones.
- Ear Tube Surgery: Placement of tubes to assist fluid drainage and equalize pressure.
Hearing Aids and Implants
For those who cannot benefit from medical or surgical treatment, hearing aids or bone conduction devices can provide significant improvements in hearing. These devices can help you hear the sounds around you, and reconnect with what matters most.
Managing Life with Conductive Hearing Loss
While conductive hearing loss can be frustrating, many individuals learn to manage their condition effectively. Consistent follow-up appointments, wearing hearing aids if prescribed, and taking preventive measures against ear infections are just a few practical steps for managing hearing loss.
Tips for Effective Communication
Here are a few strategies to improve communication with conductive hearing loss:
- Position yourself to face the person speaking to you.
- Find quiet environments for conversations.
- Ask people to speak clearly without shouting.
- Consider assistive listening devices for use in challenging listening environments.
When to Seek Help
It’s important to seek medical attention if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of conductive hearing loss. Early diagnosis and intervention can prevent long-term damage and improve day-to-day communication. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking support can lead to effective management and a return to better hearing.
From medical treatments and surgical options to assistive devices, there are a host of solutions to ensure that those with conductive hearing loss continue to lead fulfilling lives with minimal disruption. If you suspect hearing loss, visit us for a hearing test. Together we’ll find out more about your hearing loss and suggest treatment options to get you back to hearing clearly.
How to Protect Sensitive Ears in Noisy Environments
Matthew Favinger, M.S., F-AAA

Understanding the Global Impact of Hearing Loss on World Hearing Day
Matthew Favinger, M.S., F-AAA

