Hearing Loss Overview
Types & Causes of Hearing Loss
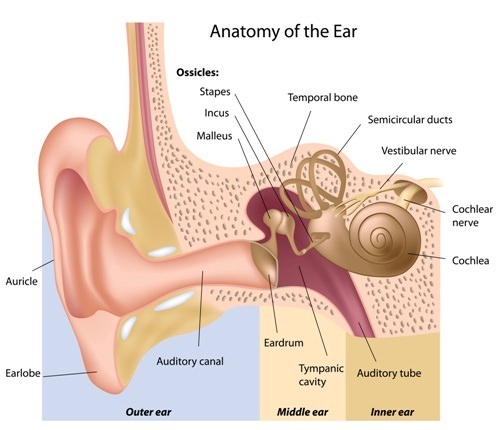
There are three distinct types of hearing loss and four classifications, which indicate the severity of the loss. Hearing loss is caused by any one of numerous conditions, which are discussed hereafter. Though this page presents many common problems, it does not attempt to explain every possibility. Difficulties in hearing can be a result of problems in any of the three sections of the ear.
What are signs of hearing loss?
Difficulty hearing in crowded rooms, asking for people to repeat what they say, difficulty on the telephone, perceiving that everyone mumbles, loud volume on the television or stereo, limited recognition of what is said, giving incorrect responses in conversation, etc. are all signs of hearing loss.
- Infection – Causes irritation, swelling and pain but usually does not cause any hearing loss unless untreated.
- Impacted earwax (cerumen) – earwax can build up and clog the ear canal, blocking the entry of sound into the inner ear. A visit to the doctor’s office to remove the earwax can provide relief.
- Retraction of the eardrum – Abnormal pressure in the ear can cause the tympanic membrane to tense up or retract, restricting its motion thus limiting the vibrations that reach the inner ear, causing a mild hearing loss.
- Perforation of the eardrum – A hole in the eardrum caused by any number of factors. Performance of the eardrum depends on where and how big the hole is. Some require surgery to repair but many heal themselves.
Find your perfect fit for hearing devices and start hearing the world around you again!
Contact us today to schedule a no-obligation hearing evaluation with our Audiologist Matthew Favinger. At your appointment, Matthew will assess your hearing and help you find the right hearing solution for you.
Contact Us